Category: gnuradio
FM transmitter through a Raspberry pi
In this post we’ll turn the Raspberry Pi into an FM transmitter in a few steps.
ATTENTION: remember that in some countries the radio transmissions of any kind are subject to federal laws and regulations.
This is a simple and very interesting article.
To turn your raspberry pi in FM transmitter we will use the rpitx of F5OEO (https://github.com/F5OEO/rpitx) , rpitx is a radio transmitter for Raspberry Pi (B, B+, PI2, PI3 and PI zero) that transmits RF directly to GPIO. It can handle frequencies from 5 KHz up to 500 MHz.
For installing do the following:
git clone https://github.com/F5OEO/rpitx
cd ./rpitx
sudo ./install.sh
The install script (install.sh) will download and install all the needed dependencies. This takes a while.
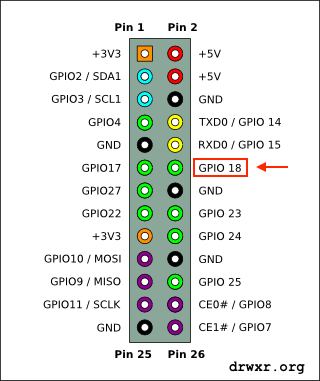
We gonna connect a ~20cm or so plain wire to GPIO 18 (which is pin 12 on header P2) to act as an antenna, and tune an FM radio.
The optimal length of the wire depends the frequency you will want to transmit.
GPIO pins (General Purpose Input/Output) are ports (pins) programmable that can be used to input and/or output data. They are mainly used to communicate with external devices like microcontroller or microprocessor.

In this article we going to transmit FM, so we gonna use the pifm.
Pifm converts an audio file (Wav, 48KHz, 1 channel, pcm_s16le codec) to Narrow band FM (12.5khz excursion) and outputs it to a .ft file. Assuming your audio file is in your current working directory.
./pifm gunsnroses.wav fm.ft
Then after execute the command that created the fm.ft, lets execute the command bellow that will transmit the audio at 92.0MHz (you can change).
sudo ./rpitx -m RF -i fm.ft -f 92000 -l
Video:
Replay Attack – Doorbell
Recently I bought a low cost wireless doorbell so I decided to analyse the RF communication and reproduce a replay attack.
To accomplish the attack I used an Ettus USRP2 N210 SDR (Software Defined Radio), a Voye wireless doorbell and GNU Radio.
The replay attack (also called as playback attack) is simple and very interesting attack, it works by simply recording a signal and then rebroadcasting it once it used a “fix code” signal to activate the doorbell.


GNU Radio
GNU Radio Companion (GRC) is a graphical tool for creating signal flow graphs and generating flow-graph source code.
More info: http://gnuradio.org/redmine/projects/gnuradio/wiki/GNURadioCompanion
Identifying the signal
Usually doorbells operates at frequencies of 433Mhz (Europe) or 315Mhz (America), it was first noticed the frequency of 433Mhz in order to get signal but nothing was found. Analyzing the 315MHz frequency we found the signal from the doorbell transmitter.
We used GQRX to clearly identify the frequency:

Capturing the signal
We recorded the signal from the doorbell transmitter in GNU Radio into a RAW file.
We’re using 2e6 (2M) as Sample Rate and this value should be used in every step.

Opening this up in AUDACITY we can see groups of pulses making up a single button press and we can identify this is a OOK (On-Off Keying) Signal.

On zooming in to a button press, we can see these button presses are made up of similar looking groups.

Notice that we’ve exported 4 sequences because the receiver has a error rate and it needs to receive more than 1 package of bits.
We gonna export using the following configuration:

Transmitting the signal
Finally, the last step was to create a flow graph to transmit the raw signal isolated.
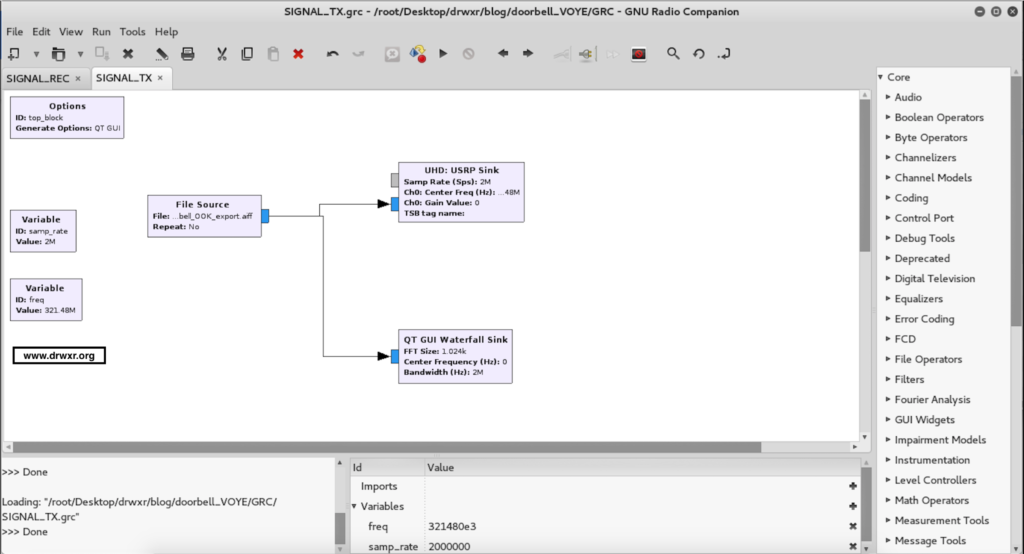
After executing the doorbell will ring…
Video of replay attack: